Pulsar Encryption
Pulsar encryption allows applications to encrypt messages at the producer and decrypt at the consumer. Encryption is performed using the public/private key pair configured by the application. Encrypted messages can only be decrypted by consumers with a valid key.
Asymmetric and symmetric encryption
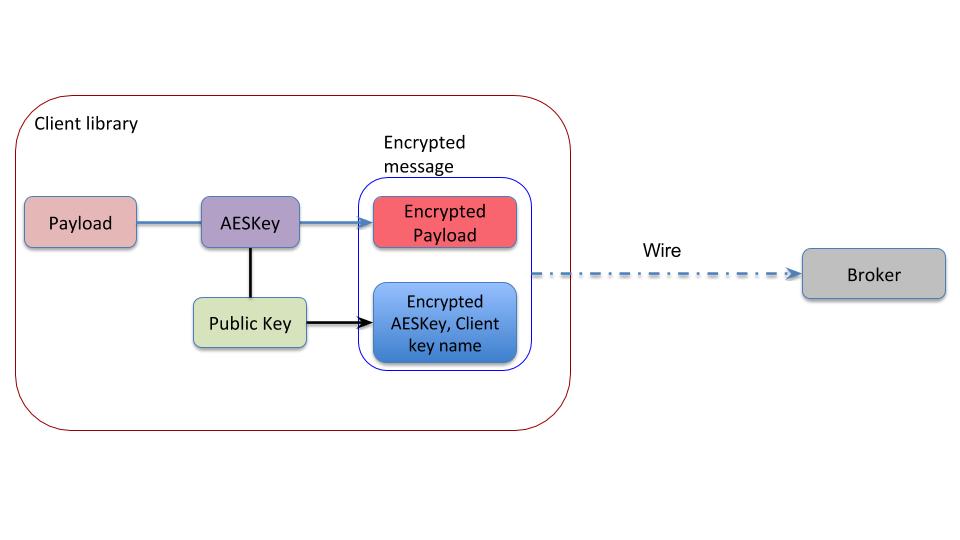
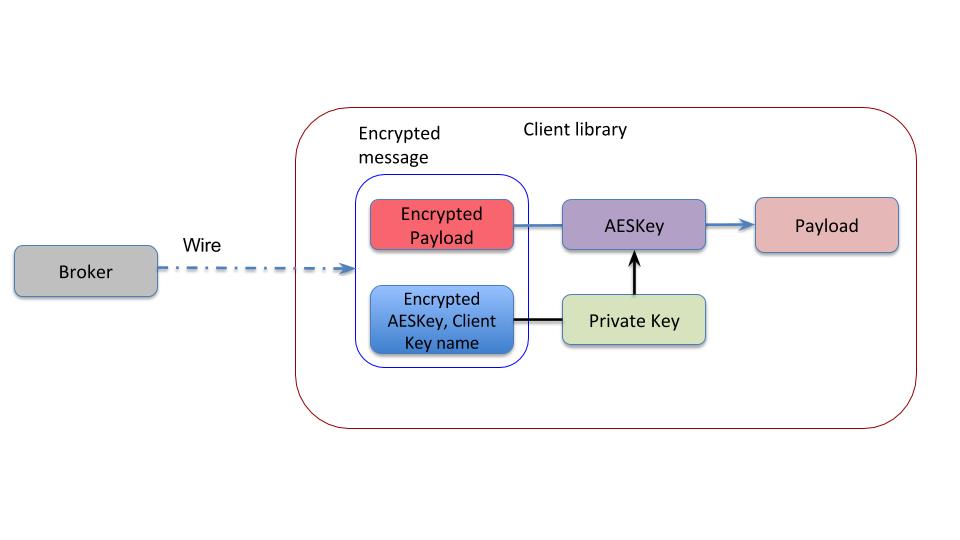
Pulsar uses dynamically generated symmetric AES key to encrypt messages(data). The AES key(data key) is encrypted using application provided ECDSA/RSA key pair, as a result there is no need to share the secret with everyone.
Key is a public/private key pair used for encryption/decryption. The producer key is the public key, and the consumer key is the private key of the key pair.
The application configures the producer with the public key. This key is used to encrypt the AES data key. The encrypted data key is sent as part of message header. Only entities with the private key(in this case the consumer) will be able to decrypt the data key which is used to decrypt the message.
A message can be encrypted with more than one key. Any one of the keys used for encrypting the message is sufficient to decrypt the message
Pulsar does not store the encryption key anywhere in the pulsar service. If you lose/delete the private key, your message is irretrievably lost, and is unrecoverable
Producer
Consumer
Here are the steps to get started:
- Create your ECDSA or RSA public/private key pair.
openssl ecparam -name secp521r1 -genkey -param_enc explicit -out test_ecdsa_privkey.pem
openssl ec -in test_ecdsa_privkey.pem -pubout -outform pkcs8 -out test_ecdsa_pubkey.pem
- Add the public and private key to the key management and configure your producers to retrieve public keys and consumers clients to retrieve private keys.
- Implement CryptoKeyReader::getPublicKey() interface from producer and CryptoKeyReader::getPrivateKey() interface from consumer, which will be invoked by Pulsar client to load the key.
- Add encryption key to producer configuration: conf.addEncryptionKey("myapp.key")
- Add CryptoKeyReader implementation to producer/consumer config: conf.setCryptoKeyReader(keyReader)
- Sample producer application:
class RawFileKeyReader implements CryptoKeyReader {
String publicKeyFile = "";
String privateKeyFile = "";
RawFileKeyReader(String pubKeyFile, String privKeyFile) {
publicKeyFile = pubKeyFile;
privateKeyFile = privKeyFile;
}
@Override
public EncryptionKeyInfo getPublicKey(String keyName, Map<String, String> keyMeta) {
EncryptionKeyInfo keyInfo = new EncryptionKeyInfo();
try {
keyInfo.setKey(Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get(publicKeyFile)));
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("ERROR: Failed to read public key from file " + publicKeyFile);
e.printStackTrace();
}
return keyInfo;
}
@Override
public EncryptionKeyInfo getPrivateKey(String keyName, Map<String, String> keyMeta) {
EncryptionKeyInfo keyInfo = new EncryptionKeyInfo();
try {
keyInfo.setKey(Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get(privateKeyFile)));
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("ERROR: Failed to read private key from file " + privateKeyFile);
e.printStackTrace();
}
return keyInfo;
}
}
PulsarClient pulsarClient = PulsarClient.create("http://localhost:8080");
ProducerConfiguration prodConf = new ProducerConfiguration();
prodConf.setCryptoKeyReader(new RawFileKeyReader("test_ecdsa_pubkey.pem", "test_ecdsa_privkey.pem"));
prodConf.addEncryptionKey("myappkey");
Producer producer = pulsarClient.createProducer("persistent://my-tenant/my-ns/my-topic", prodConf);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
producer.send("my-message".getBytes());
}
pulsarClient.close();
- Sample Consumer Application:
class RawFileKeyReader implements CryptoKeyReader {
String publicKeyFile = "";
String privateKeyFile = "";
RawFileKeyReader(String pubKeyFile, String privKeyFile) {
publicKeyFile = pubKeyFile;
privateKeyFile = privKeyFile;
}
@Override
public EncryptionKeyInfo getPublicKey(String keyName, Map<String, String> keyMeta) {
EncryptionKeyInfo keyInfo = new EncryptionKeyInfo();
try {
keyInfo.setKey(Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get(publicKeyFile)));
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("ERROR: Failed to read public key from file " + publicKeyFile);
e.printStackTrace();
}
return keyInfo;
}
@Override
public EncryptionKeyInfo getPrivateKey(String keyName, Map<String, String> keyMeta) {
EncryptionKeyInfo keyInfo = new EncryptionKeyInfo();
try {
keyInfo.setKey(Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get(privateKeyFile)));
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("ERROR: Failed to read private key from file " + privateKeyFile);
e.printStackTrace();
}
return keyInfo;
}
}
ConsumerConfiguration consConf = new ConsumerConfiguration();
consConf.setCryptoKeyReader(new RawFileKeyReader("test_ecdsa_pubkey.pem", "test_ecdsa_privkey.pem"));
PulsarClient pulsarClient = PulsarClient.create("http://localhost:8080");
Consumer consumer = pulsarClient.subscribe("persistent://my-tenant//my-ns/my-topic", "my-subscriber-name", consConf);
Message msg = null;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
msg = consumer.receive();
// do something
System.out.println("Received: " + new String(msg.getData()));
}
// Acknowledge the consumption of all messages at once
consumer.acknowledgeCumulative(msg);
pulsarClient.close();
Key rotation
Pulsar generates new AES data key every 4 hours or after a certain number of messages are published. The asymmetric public key is automatically fetched by producer every 4 hours by calling CryptoKeyReader::getPublicKey() to retrieve the latest version.
Enabling encryption at the producer application:
If you produce messages that are consumed across application boundaries, you need to ensure that consumers in other applications have access to one of the private keys that can decrypt the messages. This can be done in two ways:
- The consumer application provides you access to their public key, which you add to your producer keys
- You grant access to one of the private keys from the pairs used by producer
In some cases, the producer may want to encrypt the messages with multiple keys. For this, add all such keys to the config. Consumer will be able to decrypt the message, as long as it has access to at least one of the keys.
E.g: If messages needs to be encrypted using 2 keys myapp.messagekey1 and myapp.messagekey2,
conf.addEncryptionKey("myapp.messagekey1");
conf.addEncryptionKey("myapp.messagekey2");
Decrypting encrypted messages at the consumer application:
Consumers require access one of the private keys to decrypt messages produced by the producer. If you would like to receive encrypted messages, create a public/private key and give your public key to the producer application to encrypt messages using your public key.
Handling Failures:
- Producer/ Consumer loses access to the key
- Producer action will fail indicating the cause of the failure. Application has the option to proceed with sending unencrypted message in such cases. Call conf.setCryptoFailureAction(ProducerCryptoFailureAction) to control the producer behavior. The default behavior is to fail the request.
- If consumption failed due to decryption failure or missing keys in consumer, application has the option to consume the encrypted message or discard it. Call conf.setCryptoFailureAction(ConsumerCryptoFailureAction) to control the consumer behavior. The default behavior is to fail the request. Application will never be able to decrypt the messages if the private key is permanently lost.
- Batch messaging
- If decryption fails and the message contain batch messages, client will not be able to retrieve individual messages in the batch, hence message consumption fails even if conf.setCryptoFailureAction() is set to CONSUME.
- If decryption fails, the message consumption stops and application will notice backlog growth in addition to decryption failure messages in the client log. If application does not have access to the private key to decrypt the message, the only option is to skip/discard backlogged messages.