Pulsar Clients
Pulsar exposes a client API with language bindings for Java, Go, Python, C++ and C#. The client API optimizes and encapsulates Pulsar's client-broker communication protocol and exposes a simple and intuitive API for use by applications.
Under the hood, the current official Pulsar client libraries support transparent reconnection and/or connection failover to brokers, queuing of messages until acknowledged by the broker, and heuristics such as connection retries with backoff.
Custom client libraries
If you'd like to create your own client library, we recommend consulting the documentation on Pulsar's custom binary protocol
Client setup phase
When an application wants to create a producer/consumer, the Pulsar client library will initiate a setup phase that is composed of two steps:
- The client will attempt to determine the owner of the topic by sending an HTTP lookup request to the broker. The request could reach one of the active brokers which, by looking at the (cached) zookeeper metadata will know who is serving the topic or, in case nobody is serving it, will try to assign it to the least loaded broker.
- Once the client library has the broker address, it will create a TCP connection (or reuse an existing connection from the pool) and authenticate it. Within this connection, client and broker exchange binary commands from a custom protocol. At this point the client will send a command to create producer/consumer to the broker, which will comply after having validated the authorization policy.
Whenever the TCP connection breaks, the client will immediately re-initiate this setup phase and will keep trying with exponential backoff to re-establish the producer or consumer until the operation succeeds.
Reader interface
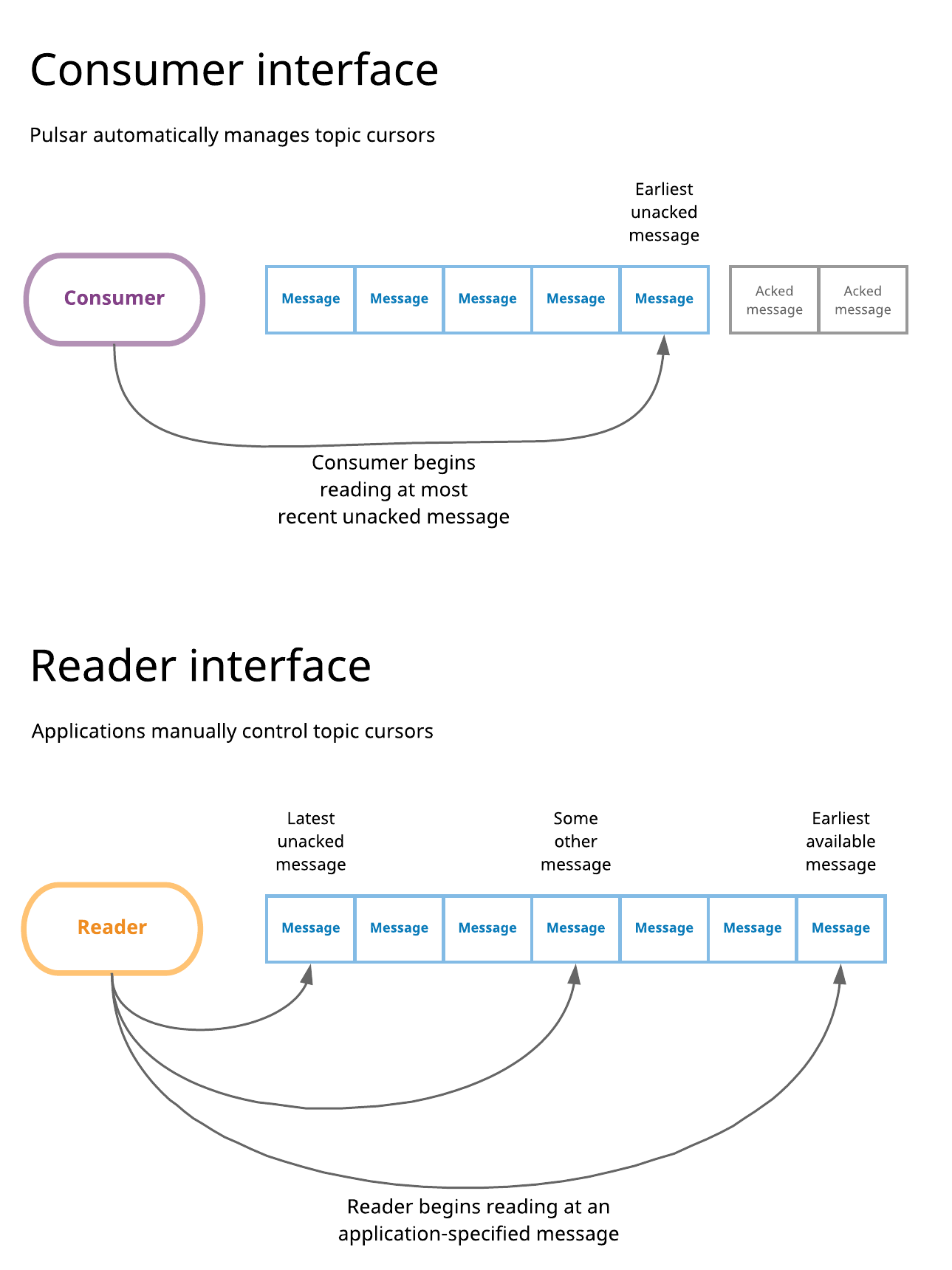
In Pulsar, the "standard" consumer interface involves using consumers to listen on topics, process incoming messages, and finally acknowledge those messages when they've been processed. Whenever a new subscription is created, it is initially positioned at the end of the topic (by default), and consumers associated with that subscription will begin reading with the first message created afterwards. Whenever a consumer connects to a topic using a pre-existing subscription, it begins reading from the earliest message un-acked within that subscription. In summary, with the consumer interface, subscription cursors are automatically managed by Pulsar in response to message acknowledgements.
The reader interface for Pulsar enables applications to manually manage cursors. When you use a reader to connect to a topic---rather than a consumer---you need to specify which message the reader begins reading from when it connects to a topic. When connecting to a topic, the reader interface enables you to begin with:
- The earliest available message in the topic
- The latest available message in the topic
- Some other message between the earliest and the latest. If you select this option, you'll need to explicitly provide a message ID. Your application will be responsible for "knowing" this message ID in advance, perhaps fetching it from a persistent data store or cache.
The reader interface is helpful for use cases like using Pulsar to provide effectively-once processing semantics for a stream processing system. For this use case, it's essential that the stream processing system be able to "rewind" topics to a specific message and begin reading there. The reader interface provides Pulsar clients with the low-level abstraction necessary to "manually position" themselves within a topic.
Internally, the reader interface is implemented as a consumer using an exclusive, non-durable subscription to the topic with a randomly-allocated name.
[ IMPORTANT ]
Unlike subscription/consumer, readers are non-durable in nature and will not prevent data in a topic from being deleted, thus it is strongly advised that data retention be configured. If data retention for a topic is not configured for an adequate amount of time, messages that the reader has not yet read might be deleted . This will cause readers to essentially skip messages. Configuring the data retention for a topic guarantees the reader with have a certain duration to read a message.
Please also note that a reader can have a "backlog", but the metric is just to allow users to know how behind the reader is and is not considered for any backlog quota calculations.
Non-partitioned topics only
The reader interface for Pulsar cannot currently be used with partitioned topics.
Here's a Java example that begins reading from the earliest available message on a topic:
import org.apache.pulsar.client.api.Message;
import org.apache.pulsar.client.api.MessageId;
import org.apache.pulsar.client.api.Reader;
// Create a reader on a topic and for a specific message (and onward)
Reader<byte[]> reader = pulsarClient.newReader()
.topic("reader-api-test")
.startMessageId(MessageId.earliest)
.create();
while (true) {
Message message = reader.readNext();
// Process the message
}
To create a reader that will read from the latest available message:
Reader<byte[]> reader = pulsarClient.newReader()
.topic(topic)
.startMessageId(MessageId.latest)
.create();
To create a reader that will read from some message between earliest and latest:
byte[] msgIdBytes = // Some byte array
MessageId id = MessageId.fromByteArray(msgIdBytes);
Reader<byte[]> reader = pulsarClient.newReader()
.topic(topic)
.startMessageId(id)
.create();