Use cases
Below you can review common use cases for the broker load balancer.
Spread workloads for scaling
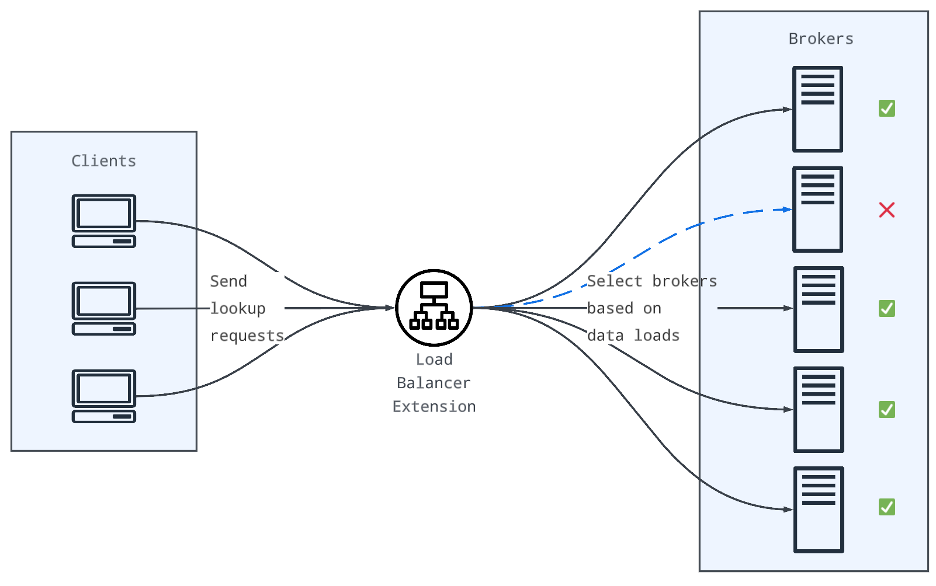
The broker load balancer routes incoming data processing requests to available brokers for stable performance, making it ideal for quick horizontal scaling — whether in response to sudden traffic spikes or deliberate business expansions. In this case, you can run high-traffic applications with a lot of concurrent data requests in a fast and reliable manner.
High availability with fault tolerance
The broker load balancer can increase cluster availability by re-routing data loads to other available brokers if a broker fails. This failover mechanism ensures the availability of the whole system.
Related topics
-
To get a comprehensive understanding and discover the key insights, see Broker load balancing | Overview.
-
To explore functionalities, see Broker load balancing | Features.
-
To understand advantages, see Broker load balancing | Benefits.
-
To learn essential fundamentals, see Broker load balancing | Concepts.
-
To review various versions of broker load balancers, see Broker load balancing | Types.
-
To get up quickly, see Broker load balancing | Quick start.
-
To migrate one broker load balancer type to another, see Broker load balancing | Migration.