Overview of tiered storage
Pulsar's Tiered Storage feature allows older backlog data to be moved from BookKeeper to long-term and cheaper storage, while still allowing clients to access the backlog as if nothing has changed.
- Tiered storage uses Apache jclouds to support Amazon S3, GCS (Google Cloud Storage), Azure and Aliyun OSS for long-term storage.
- Read how to Use AWS S3 offloader with Pulsar;
- Read how to Use GCS offloader with Pulsar;
- Read how to Use Azure BlobStore offloader with Pulsar;
- Read how to Use Aliyun OSS offloader with Pulsar;
- Read how to Use S3 offloader with Pulsar.
- Tiered storage uses Apache Hadoop to support filesystems for long-term storage.
- Read how to Use filesystem offloader with Pulsar.
The AWS S3 offloader registers specific AWS metadata, such as regions and service URLs and requests bucket location before performing any operations. If you cannot access the Amazon service, you can use the S3 offloader instead since it is an S3 compatible API without the metadata.
When to use tiered storage?
Tiered storage should be used when you have a topic for which you want to keep a very long backlog for a long time.
For example, if you have a topic containing user actions that you use to train your recommendation systems, you may want to keep that data for a long time, so that if you change your recommendation algorithm, you can rerun it against your full user history.
How to install tiered storage offloaders?
Pulsar releases a separate binary distribution, containing the tiered storage offloaders. To enable those offloaders, you need to complete the following steps.
- Download the offloaders tarball release.
wget https://archive.apache.org/dist/pulsar/pulsar-4.1.3/apache-pulsar-offloaders-4.1.3-bin.tar.gz
- Untar the offloaders package and copy the offloaders as
offloadersin the pulsar directory.
tar xvfz apache-pulsar-offloaders-4.1.3-bin.tar.gz
mv apache-pulsar-offloaders-4.1.3/offloaders offloaders
ls offloaders
# tiered-storage-file-system-4.1.3.nar
# tiered-storage-jcloud-4.1.3.nar
For more information on how to configure tiered storage, see Tiered storage cookbook.
- If you are running Pulsar in a bare metal cluster, make sure that
offloaderstarball is unzipped in every broker's pulsar directory. - If you are running Pulsar in Docker or deploying Pulsar using a docker image (e.g. K8S), you can use the
apachepulsar/pulsar-allimage instead of theapachepulsar/pulsarimage.apachepulsar/pulsar-allimage has already bundled tiered storage offloaders.
How does tiered storage work?
A topic in Pulsar is backed by a log, known as a managed ledger. This log is composed of an ordered list of segments. Pulsar only writes to the final segment of the log. All previous segments are sealed. The data within the segment is immutable. This is known as a segment-oriented architecture.
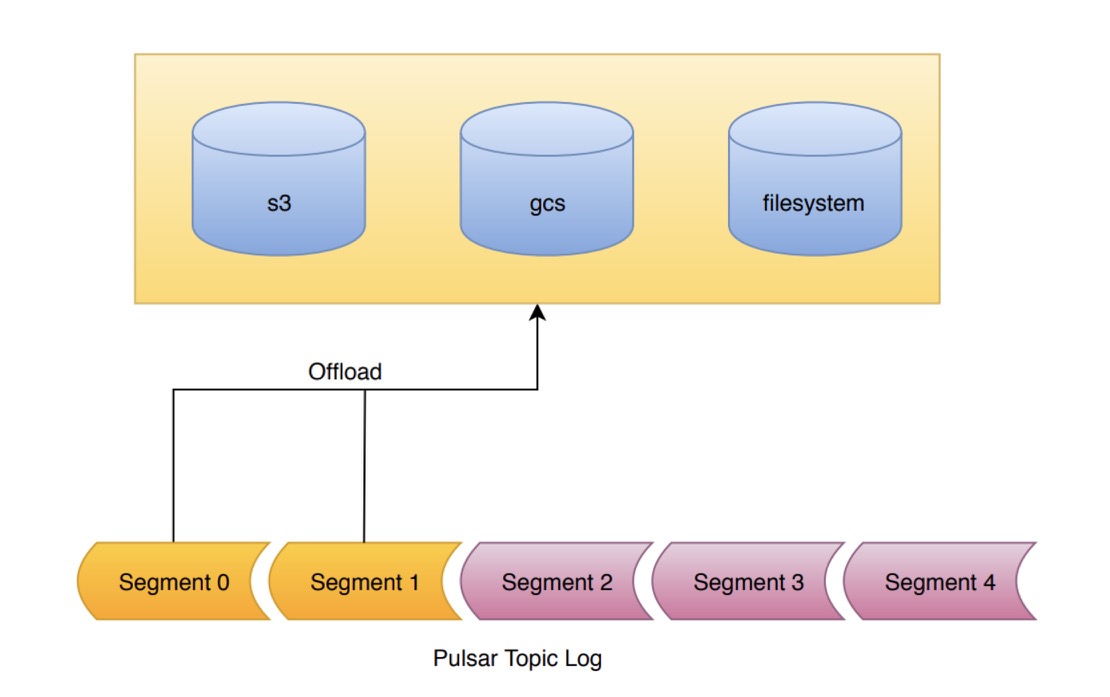
Tiered storage works as follows:
- The tiered storage offloading mechanism takes advantage of the segment-oriented architecture.
When offloading is requested, the segments of the log are copied one by one to tiered storage. All segments of the log (apart from the current segment) written to tiered storage can be offloaded.
- Data written to BookKeeper is replicated to 3 physical machines by default.
However, once a segment is sealed in BookKeeper, it becomes immutable and can be copied to long-term storage. Long-term storage has the potential to achieve significant cost savings.
-
Before offloading ledgers to long-term storage, you need to configure buckets, credentials, and other properties for the cloud storage service.
-
Additionally, Pulsar uses multi-part objects to upload the segment data and brokers may crash while uploading the data.
It is recommended that you add a life cycle rule for your bucket to expire incomplete multi-part upload after a day or two days to avoid getting charged for incomplete uploads.
-
Moreover, you can trigger the offloading operation manually (via REST API or CLI) or automatically (via CLI).
-
After transferring ledgers to long-term storage, the messages within these ledgers remain accessible to Pulsar consumers and readers, ensuring transparency in data retrieval.
For more information about tiered storage for Pulsar topics, see PIP-17 and offload metrics.